Java Libraries
Copy JAR files which are listed below:
antlr-2.7.7.jar
classmate-1.3.4.jar
commons-lang3-3.6.jar
commons-logging-1.1.3.jar
dom4j-1.6.1.jar
ehcache-core-2.6.11.jar
geolatte-geom-1.1.0.jar
hibernate-commons-annotations-5.0.1.Final.jar
hibernate-core-5.2.11.Final.jar
hibernate-ehcache-5.2.12.Final.jar
hibernate-ejb3-persistence.jar
hibernate-enhance-maven-plugin-4.3.7.Final.jar
hibernate-entitymanager.jar
hibernate-java8-5.2.11.Final.jar
hibernate-jpa-2.1-api-1.0.0.Final.jar
hibernate-spatial-5.2.11.Final.jar
hibernate-validator-6.0.2.Final.jar
javassist-3.16.1-GA.jar
jboss-logging-3.3.1.Final.jar
jboss-transaction-api_1.1_spec-1.0.1.Final.jar
jts-1.11.jar
mysql-connector-java-5.1.36.jar
slf4j-api-1.7.21.jar
Create Database
Create a database with the name is hibernate5. This database have 2 tables: Category table and Product table. Category table and Product table have a One to Many. One category can have many products and One product belongs to one and only one category.
--
-- Table structure for table `category`
--
CREATE TABLE `category` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(250) NOT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
--
-- Dumping data for table `category`
--
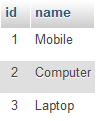
INSERT INTO `category` (`name`) VALUES('Mobile');
INSERT INTO `category` (`name`) VALUES('Computer');
INSERT INTO `category` (`name`) VALUES('Laptop');
--
-- Table structure for table `product`
--
CREATE TABLE `product` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(250) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`price` decimal(10,1) NOT NULL,
`quantity` int(11) NOT NULL,
`description` text COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`photo` varchar(250) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`featured` tinyint(1) NOT NULL,
`categoryid` int(11) NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (`categoryid`) REFERENCES `category` (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_unicode_ci;
--
-- Dumping data for table `product`
--
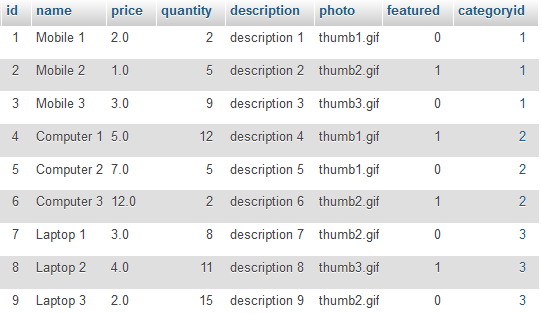
INSERT INTO `product` (`name`, `price`, `quantity`, `description`, `photo`, `categoryid`, `featured`) VALUES('Mobile 1', '2.0', 2, 'description 1', 'thumb1.gif', 1, 0);
INSERT INTO `product` (`name`, `price`, `quantity`, `description`, `photo`, `categoryid`, `featured`) VALUES('Mobile 2', '1.0', 5, 'description 2', 'thumb2.gif', 1, 1);
INSERT INTO `product` (`name`, `price`, `quantity`, `description`, `photo`, `categoryid`, `featured`) VALUES('Mobile 3', '3.0', 9, 'description 3', 'thumb3.gif', 1, 0);
INSERT INTO `product` (`name`, `price`, `quantity`, `description`, `photo`, `categoryid`, `featured`) VALUES('Computer 1', '5.0', 12, 'description 4', 'thumb1.gif', 2, 1);
INSERT INTO `product` (`name`, `price`, `quantity`, `description`, `photo`, `categoryid`, `featured`) VALUES('Computer 2', '7.0', 5, 'description 5', 'thumb1.gif', 2, 0);
INSERT INTO `product` (`name`, `price`, `quantity`, `description`, `photo`, `categoryid`, `featured`) VALUES('Computer 3', '12.0', 2, 'description 6', 'thumb2.gif', 2, 1);
INSERT INTO `product` (`name`, `price`, `quantity`, `description`, `photo`, `categoryid`, `featured`) VALUES('Laptop 1', '3.0', 8, 'description 7', 'thumb2.gif', 3, 0);
INSERT INTO `product` (`name`, `price`, `quantity`, `description`, `photo`, `categoryid`, `featured`) VALUES('Laptop 2', '4.0', 11, 'description 8', 'thumb3.gif', 3, 1);
INSERT INTO `product` (`name`, `price`, `quantity`, `description`, `photo`, `categoryid`, `featured`) VALUES('Laptop 3', '2.0', 15, 'description 9', 'thumb2.gif', 3, 0);
Category Table
Product Table
Entities Class
Create two entities classes – Category.java and Product.java, to represent the above tables
Category.java
package entities;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import static javax.persistence.GenerationType.IDENTITY;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "category")
public class Category implements java.io.Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Set<Product> products = new HashSet<Product>(0);
public Category() {
}
public Category(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Category(String name, Set<Product> products) {
this.name = name;
this.products = products;
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id", unique = true, nullable = false)
public Integer getId() {
return this.id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Column(name = "name", nullable = false, length = 250)
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@OneToMany(fetch = FetchType.LAZY, mappedBy = "category")
public Set<Product> getProducts() {
return this.products;
}
public void setProducts(Set<Product> products) {
this.products = products;
}
}
Product.java
package entities;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import static javax.persistence.GenerationType.IDENTITY;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "product")
public class Product implements java.io.Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private BigDecimal price;
private int quantity;
private String description;
private String photo;
private boolean featured;
private Category category;
public Product() {
}
public Product(Integer id, String name, BigDecimal price) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id", unique = true, nullable = false)
public Integer getId() {
return this.id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Column(name = "name", nullable = false, length = 250)
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Column(name = "price", nullable = false, precision = 10, scale = 1)
public BigDecimal getPrice() {
return this.price;
}
public void setPrice(BigDecimal price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Column(name = "quantity", nullable = false)
public int getQuantity() {
return this.quantity;
}
public void setQuantity(int quantity) {
this.quantity = quantity;
}
@Column(name = "description", nullable = false, length = 65535)
public String getDescription() {
return this.description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
@Column(name = "photo", nullable = false, length = 250)
public String getPhoto() {
return this.photo;
}
public void setPhoto(String photo) {
this.photo = photo;
}
@Column(name = "featured", nullable = false)
public boolean isFeatured() {
return this.featured;
}
public void setFeatured(boolean featured) {
this.featured = featured;
}
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "categoryid", nullable = false)
public Category getCategory() {
return category;
}
public void setCategory(Category category) {
this.category = category;
}
}
Hibernate Configuration File
Puts Category.java and Product.java in your Hibernate configuration file, and also MySQL connection details.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="hibernate.enable_lazy_load_no_trans">true</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.password">123456</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hibernate5</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property>
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.spatial.dialect.mysql.MySQLSpatialDialect</property>
<property name="hibernate.current_session_context_class">thread</property>
<mapping class="entities.Product" />
<mapping class="entities.Category" />
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>
Create HibernateUtil class
The HibernateUtil class helps in creating the SessionFactory from the Hibernate configuration file. The SessionFactory is threadsafe, so it is not necessary to obtain one for each thread.
package criteria_query;
import org.hibernate.*;
import org.hibernate.boot.*;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.*;
public class HibernateUtil {
private static final SessionFactory sessionFactory;
static {
try {
StandardServiceRegistry standardRegistry = new
StandardServiceRegistryBuilder()
.configure("hibernate.cfg.xml")
.build();
Metadata metaData = new MetadataSources(
standardRegistry)
.getMetadataBuilder()
.build();
sessionFactory = metaData.getSessionFactoryBuilder().build();
} catch (Throwable th) {
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(th);
}
}
public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
return sessionFactory;
}
}
Create ProductModel class
The ProductModel class contains methods to interact with the database.
package criteria_query;
import java.util.*;
import javax.persistence.criteria.CriteriaBuilder;
import javax.persistence.criteria.CriteriaQuery;
import javax.persistence.criteria.Root;
import org.hibernate.*;
import entities.*;
public class ProductModel {
private SessionFactory sessionFactory = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory();
public List<Product> limit(int n) {
List<Product> products = null;
Session session = sessionFactory.openSession();
Transaction transaction = null;
try {
transaction = session.beginTransaction();
CriteriaBuilder builder = session.getCriteriaBuilder();
CriteriaQuery<Product> query = builder.createQuery(Product.class);
Root<Product> root = query.from(Product.class);
query.select(root);
query.orderBy(builder.desc(root.get("price")));
products = session.createQuery(query)
.setMaxResults(n)
.getResultList();
transaction.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
products = null;
if (transaction != null) {
transaction.rollback();
}
} finally {
session.close();
}
return products;
}
}
Run It
package criteria_query;
import java.util.List;
import entities.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProductModel productModel = new ProductModel();
List<Product> products = productModel.limit(2);
for (Product product : products) {
System.out.println("Id: " + product.getId());
System.out.println("Name: " + product.getName());
System.out.println("Price: " + product.getPrice());
System.out.println("=======================");
}
}
}
Output
Id: 6
Name: Computer 3
Price: 12.0
=======================
Id: 5
Name: Computer 2
Price: 7.0
=======================


