Create Database
Create a database named SecurityASPNETCoreMVC. This database have 3 tables: Role, Account and Account_Role as below:
USE LearnASPNETMVCWithRealApps
GO
CREATE TABLE Account (
Id int IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
Username varchar(250) NULL,
Password varchar(250) NULL,
FullName varchar(250) NULL,
Enable bit NULL,
)
GO
CREATE TABLE Role(
Id int IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
Name varchar(250) NULL
)
GO
CREATE TABLE Account_Role(
AccountId int NOT NULL,
RoleId int NOT NULL,
Enable bit NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(AccountId, RoleId),
FOREIGN KEY(AccountId) REFERENCES Account(Id),
FOREIGN KEY(RoleId) REFERENCES Role(Id)
)
GO
INSERT INTO Account(Id, Username, Password, FullName, Enable) VALUES (1, 'acc1', '$2a$04$G9AnawJboy8aYDBFeU6.6.2CuwAXN7OOQU2YYA29Xk/TgHI034UVW', 'Account 1', 1)
INSERT INTO Account(Id, Username, Password, FullName, Enable) VALUES (2, 'acc2', '$2a$04$G9AnawJboy8aYDBFeU6.6.2CuwAXN7OOQU2YYA29Xk/TgHI034UVW', 'Account 2', 1)
INSERT INTO Account(Id, Username, Password, FullName, Enable) VALUES (3, 'acc3', '$2a$04$G9AnawJboy8aYDBFeU6.6.2CuwAXN7OOQU2YYA29Xk/TgHI034UVW', 'Account 3', 1)
GO
INSERT INTO Role(Id, Name) VALUES (1, 'SuperAdmin')
INSERT INTO Role(Id, Name) VALUES (2, 'Admin')
INSERT INTO Role(Id, Name) VALUES (3, 'Employee')
GO
INSERT INTO Account_Role(AccountId, RoleId, Enable) VALUES (1, 1, 1)
INSERT INTO Account_Role(AccountId, RoleId, Enable) VALUES (1, 2, 1)
INSERT INTO Account_Role(AccountId, RoleId, Enable) VALUES (2, 2, 1)
INSERT INTO Account_Role(AccountId, RoleId, Enable) VALUES (1, 3, 1)
INSERT INTO Account_Role(AccountId, RoleId, Enable) VALUES (2, 3, 1)
INSERT INTO Account_Role(AccountId, RoleId, Enable) VALUES (3, 3, 1)
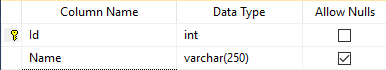
Structure of Role Table
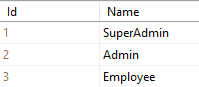
Data of Role Table
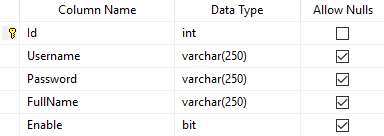
Structure of Account Table
Data of Account Table
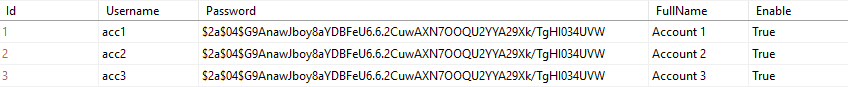
Structure of Account_Role Table
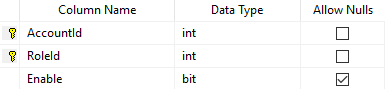
Data of Account_Role Table
Create ASP.NET Core MVC Project
On the Visual Studio, create new ASP.NET Core Web Application project
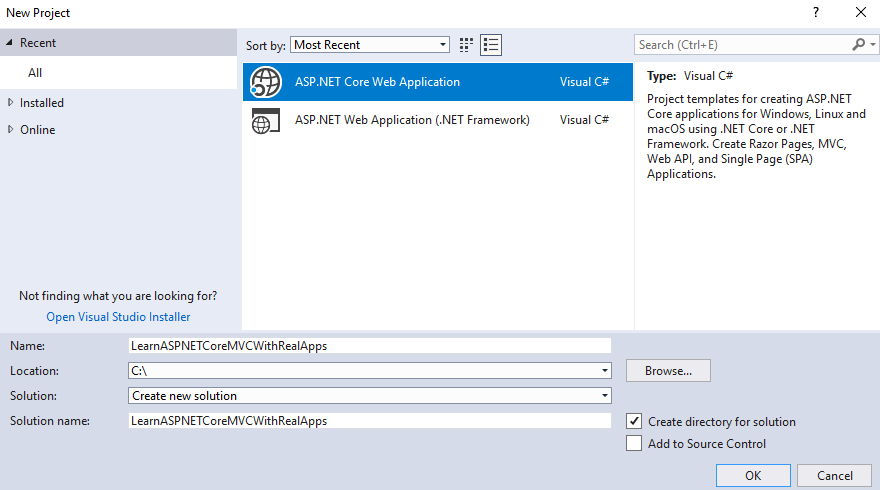
Select Empty Template
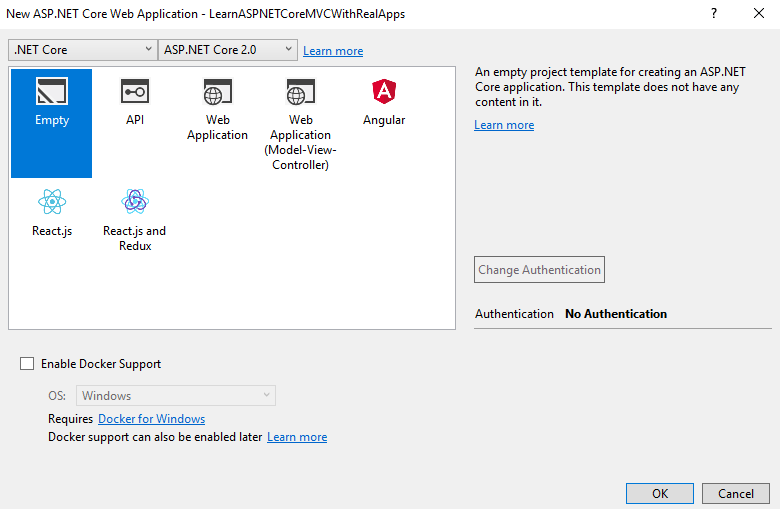
Click Ok button to Finish
Add Configurations
Open Startup.cs file and add new configurations as below:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.Cookies;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
namespace LearnASPNETCoreMVCWithRealApps
{
public class Startup
{
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddAuthentication(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)
.AddCookie(options =>
{
options.LoginPath = "/Account/Index";
options.LogoutPath = "/Account/SignOut";
options.AccessDeniedPath = "/Account/AccessDenied";
});
services.AddMvc();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseMvc();
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseMvc(routes =>
{
routes.MapRoute(
name: "default",
template: "{controller=Account}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
}
}
}
Create AppSettings File
Select Project and right click to select Add\New Item Menu
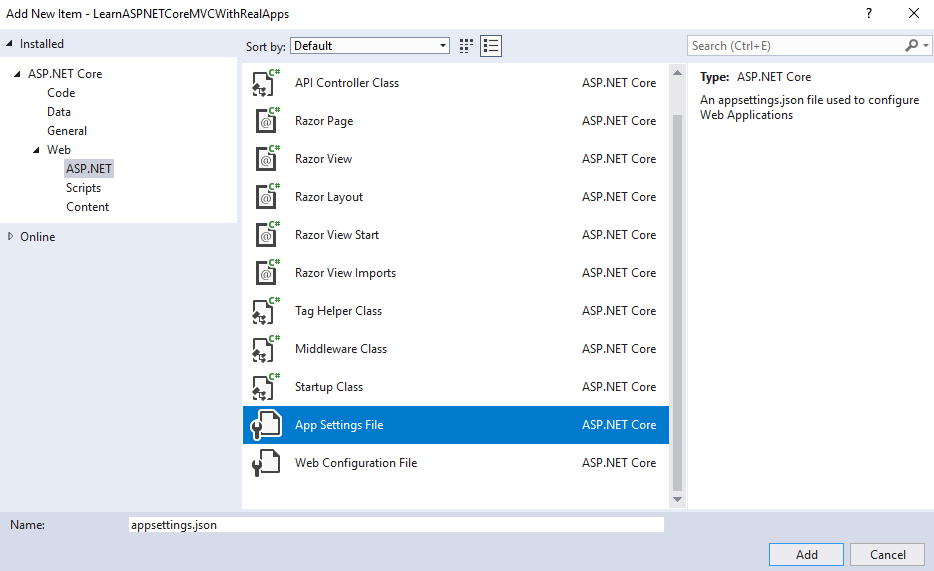
Select Web\ASP.NET in left side. Select App Settings File item and click Add button to Finish
In appsettings.json file and new configurations as below:
{
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "Server=.;Database=SecurityASPNETCoreMVC;user id=sa;password=123456"
}
}
Entities Class
Create new folder named Models. In this folder, create new class as below:
Account Entity
Create new class named Account.cs as below:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace LearnASPNETCoreMVCWithRealApps.Models
{
[Table("Account")]
public partial class Account
{
public Account()
{
AccountRoles = new HashSet<AccountRole>();
}
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Username { get; set; }
public string Password { get; set; }
public string FullName { get; set; }
public bool? Enable { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<AccountRole> AccountRoles { get; set; }
}
}
Role Entity
Create new class named Role.cs as below:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace LearnASPNETCoreMVCWithRealApps.Models
{
[Table("Role")]
public partial class Role
{
public Role()
{
AccountRoles = new HashSet<AccountRole>();
}
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public virtual ICollection<AccountRole> AccountRoles { get; set; }
}
}
AccountRole Entity
Create new class named AccountRole.cs as below:
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
namespace LearnASPNETCoreMVCWithRealApps.Models
{
[Table("Account_Role")]
public partial class AccountRole
{
public int AccountId { get; set; }
public int RoleId { get; set; }
public bool? Enable { get; set; }
public virtual Account Account { get; set; }
public virtual Role Role { get; set; }
}
}
DataContext Class
In Models folder, create new class named DatabaseContext.cs as below:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using System.IO;
namespace LearnASPNETCoreMVCWithRealApps.Models
{
public partial class DatabaseContext : DbContext
{
public DatabaseContext()
{
}
public DatabaseContext(DbContextOptions<DatabaseContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
public virtual DbSet<Account> Accounts { get; set; }
public virtual DbSet<AccountRole> AccountRoles { get; set; }
public virtual DbSet<Role> Roles { get; set; }
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
if (!optionsBuilder.IsConfigured)
{
var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder()
.SetBasePath(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory())
.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json");
var configuration = builder.Build();
optionsBuilder.UseLazyLoadingProxies()
.UseSqlServer(configuration["ConnectionStrings:DefaultConnection"]);
}
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Account>(entity =>
{
entity.Property(e => e.FullName)
.HasMaxLength(250)
.IsUnicode(false);
entity.Property(e => e.Password)
.HasMaxLength(250)
.IsUnicode(false);
entity.Property(e => e.Username)
.HasMaxLength(250)
.IsUnicode(false);
});
modelBuilder.Entity<AccountRole>(entity =>
{
entity.HasKey(e => new { e.RoleId, e.AccountId });
entity.ToTable("Account_Role");
entity.HasOne(d => d.Account)
.WithMany(p => p.AccountRoles)
.HasForeignKey(d => d.AccountId)
.OnDelete(DeleteBehavior.ClientSetNull)
.HasConstraintName("FK_Account_Role_Account");
entity.HasOne(d => d.Role)
.WithMany(p => p.AccountRoles)
.HasForeignKey(d => d.RoleId)
.OnDelete(DeleteBehavior.ClientSetNull)
.HasConstraintName("FK_Account_Role_Role");
});
modelBuilder.Entity<Role>(entity =>
{
entity.Property(e => e.Name)
.HasMaxLength(250)
.IsUnicode(false);
});
}
}
}
Security Manager
Create Security folder in project. This folder contains class need for security in ASP.NET Core MVC as below:
SecurityManager Class
using LearnASPNETCoreMVCWithRealApps.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.Cookies;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Security.Claims;
namespace LearnASPNETCoreMVCWithRealApps.Security
{
public class SecurityManager
{
public async void SignIn(HttpContext httpContext, Account account)
{
ClaimsIdentity claimsIdentity = new ClaimsIdentity(getUserClaims(account), CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme);
ClaimsPrincipal claimsPrincipal = new ClaimsPrincipal(claimsIdentity);
await httpContext.SignInAsync(CookieAuthenticationDefaults.AuthenticationScheme, claimsPrincipal);
}
public async void SignOut(HttpContext httpContext)
{
await httpContext.SignOutAsync();
}
private IEnumerable<Claim> getUserClaims(Account account)
{
List<Claim> claims = new List<Claim>();
claims.Add(new Claim(ClaimTypes.Name, account.Username));
account.AccountRoles.ToList().ForEach(ac =>
{
claims.Add(new Claim(ClaimTypes.Role, ac.Role.Name));
});
return claims;
}
}
}
Create Controllers
Create new folder named Controllers. In this folder, create new controllers as below:
Demo Controller
Create new controller named DemoController.cs as below:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace LearnASPNETCoreMVCWithRealApps.Controllers
{
public class DemoController : Controller
{
[AllowAnonymous]
public IActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
[Authorize(Roles = "SuperAdmin")]
public IActionResult Work1()
{
return View("Work1");
}
[Authorize(Roles = "SuperAdmin,Admin")]
public IActionResult Work2()
{
return View("Work2");
}
[Authorize(Roles = "SuperAdmin,Admin,Employee")]
public IActionResult Work3()
{
return View("Work3");
}
}
}
Account Controller
Create new controller named AccountController.cs as below:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using LearnASPNETCoreMVCWithRealApps.Models;
using LearnASPNETCoreMVCWithRealApps.Security;
using System.Linq;
namespace LearnASPNETCoreMVCWithRealApps.Controllers
{
public class AccountController : Controller
{
private DatabaseContext db = new DatabaseContext();
private SecurityManager securityManager = new SecurityManager();
public IActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
[HttpPost]
public IActionResult Login(string username, string password)
{
var account = processLogin(username, password);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(username) || string.IsNullOrEmpty(password) || account == null)
{
ViewBag.error = "Invalid";
return View("Index");
}
else
{
securityManager.SignIn(this.HttpContext, account);
return RedirectToAction("welcome");
}
}
private Account processLogin(string username, string password)
{
var account = db.Accounts.SingleOrDefault(a => a.Username.Equals(username) && a.Enable == true);
if (account != null)
{
if (BCrypt.Net.BCrypt.Verify(password, account.Password))
{
return account;
}
}
return null;
}
public IActionResult Welcome()
{
return View("Welcome");
}
public IActionResult AccessDenied()
{
return View("AccessDenied");
}
public IActionResult SignOut()
{
securityManager.SignOut(this.HttpContext);
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
}
}
Create View
Create new folder named Views. In this folder, create new views as below:
Account Views
Create new folder named Account folder. In this folder, create new views as below:
Index View
Create new view named Index.cshtml as below:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
<title>Login</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Login Page</h3>
@ViewBag.error
<form method="post" asp-controller="account" asp-action="login">
<table>
<tr>
<td>Username</td>
<td>
<input type="text" name="username" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Password</td>
<td>
<input type="password" name="password" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td>
<input type="submit" value="Login" />
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Welcome View
Create new view named Welcome.cshtml as below:
@using System.Security.Claims;
@{
var userId = User.FindFirst(ClaimTypes.Name);
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
<title>Welcome</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Welcome Page</h3>
Welcome @userId.Value
<br />
<a asp-controller="account" asp-action="SignOut">Logout</a>
</body>
</html>
Access Denied View
Create new view named AccessDenied.cshtml as below:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
<title>Access Denied</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Access Denied Page</h3>
</body>
</html>
Demo Views
Createw new folder named Demo. In this folder, create new views as below:
Index View
Create new view named Index.cshtml as below:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
<title>Index</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Index Page</h3>
</body>
</html>
Work1 View
Create new view named Work1.cshtml as below:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
<title>Work 1</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Work 1 Page</h3>
</body>
</html>
Work2 View
Create new view named Work2.cshtml as below:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
<title>Work 2</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Work 2 Page</h3>
</body>
</html>
Work3 View
Create new view named Work3.cshtml as below:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" />
<title>Work 3</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>Work 3 Page</h3>
</body>
</html>
Structure of ASP.NET MVC Core Project
Run Application
-
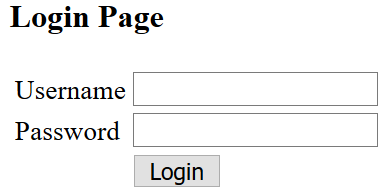
Access Index action in Account controller with following url: http://localhost:49328/Account/Index
Output
-
Test access Index action in Demo controller without account with url: http://localhost:49328/Demo/Index
Output
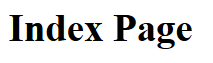
-
Test access Work1 action in Demo controller without account with url: http://localhost:49328/Demo/Work1
Output

-
Test access Work2 action in Demo controller without account with url: http://localhost:49328/Demo/Work2
Output

-
Test access Work3 action in Demo controller without account with url: http://localhost:49328/Demo/Work3
Output

-
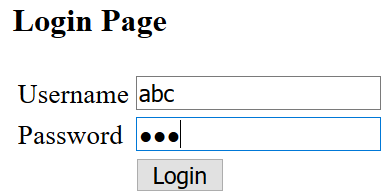
Test login with invalid account: username is abc and password is 456
Output
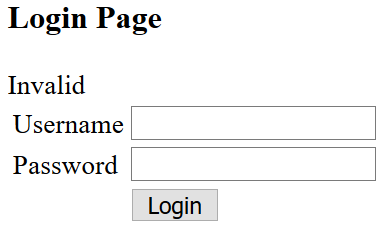
-
Test login with valid account: username is acc2 and password is 123. This account have roles: admin and employee
Output
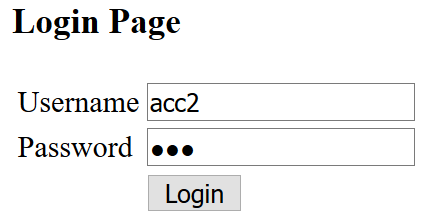
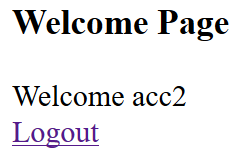
-
Use acc2 has logged access Work1 action in Demo controller with url: http://localhost:49328/Demo/Work1
Output

-
Use acc2 has logged access Work2 action in Demo controller with url: http://localhost:49328/Demo/Work2
Output
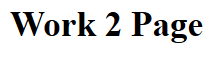
-
Use acc2 has logged access Work3 action in Demo controller with url: http://localhost:49328/Demo/Work3
Output